The coronavirus may be a crisis, but the air is cleaner. This is evident to TU Delft researchers from Tropomi images from the Copernicus Sentinel-5P satellite.
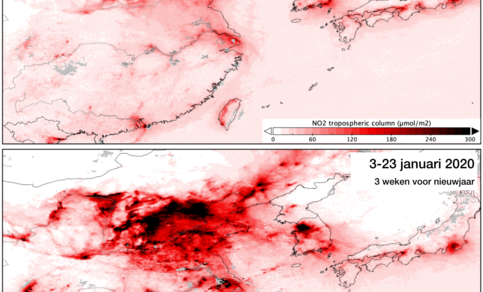
The concentration of NO2 measured above China in the three weeks before (bottom) and three weeks after (top) Chinese New Year. The coronavirus outbreak and the prevention measures taken coincide with the week in which the new year fell. (Source: EU/ESA/KN
The coronavirus is leading to huge drops in air pollution. Researchers from TU Delft and the KNMI (Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute) are observing this decrease from space from the Dutch Tropomi instrument on the Copernicus Sentinel-5P satellite.
The changes caused by coronavirus prevention measures are mostly visible in Tropomi’s NO2 (nitrogen dioxide) measurements. In China, the researchers are measuring a major reduction in the amount of NO2 since Chinese New Year (see photo above) when the prevention measures took effect. On average, they see a reduction of concentrations of about 35% across the country compared to 2019. For individual cities, this can go up to 50% to 60%.
‘We have never seen such a dramatic drop in pollution’
Prof. Pieternel Levelt of the Department of Civil Engineering and Geosciences (CEG) is the scientific initiator of the Tropomi satellite instrument. “We have never seen such a dramatic drop in pollution. People around the world are looking at our measurements. What is happening here is unique.”
More recently, the researchers have also started looking at what is happening in Europe. The outbreak of the coronavirus in Italy, and in particular to the north, in the Po Valley, have also led to prevention measures. ‘In this region we see a strong reduction in concentrations compared to last year,’ the researchers write (article in Dutch) on the KNMI website. See the image below and ESA’s animation. In Milan, the concentration was about 40% lower at the end of February and into March as in the same period last year.
The reduction measured by Tropomi is confirmed by the analysis of the concentrations of NO2 on the ground by the Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service. Given the prevention measures taken in the Netherlands, the researchers expect to observe the effects on NO2 here too in the next few weeks.
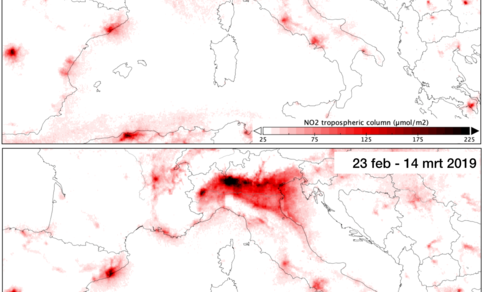
The concentrations of NO2 in Italy in the period from 23 February to 14 March in 2019 (bottom) compared to the same period in 2020 (top). (Source: EU/ESA/KNMI
Do you have a question or comment about this article?
tomas.vandijk@tudelft.nl

Comments are closed.